There are following types of conditional statements in C :
- if statement
- if - else statement
- nested if-else statement
- if -else if ladder
- switch statement
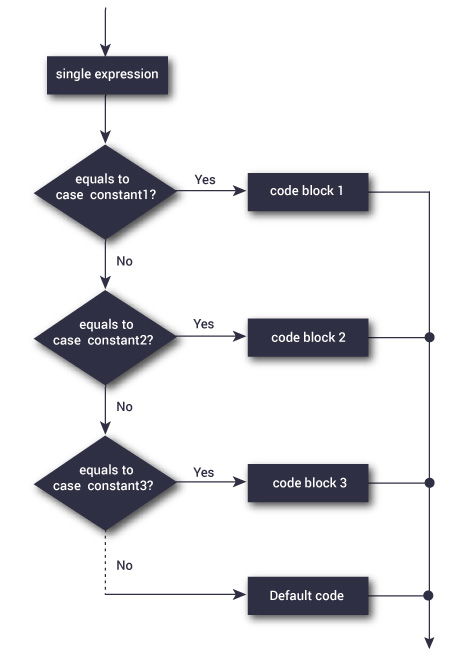
5. Switch statement -The switch statement allows us to execute the case according to or as per the needs of user's choice among many the alternatives .
How does the switch statement work?
- The expression is checked once and compared with the values of each case label.
- If the value of the expression is equal to any of the constant , the statements in that case are executed until the break is encountered.
- If the constant according to the users demand is not found, then the default statements are executed.
- If we do not use break, then all statements of the case after that case are executed.
- The default statement inside the switch statement is optional.
Syntax :
switch (expression)
{
case constant1:
// C statements
break;
case constant2:
// C statements
break;
.
.
default:
// C default statements
}
Flow Diagram of Switch statement
Example of Switch case in C
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int operation="1";
switch(operation)
{
case 1 :
printf("You have selected operation 1."); //diplayed as output
break;
case 2 :
printf("You have selected operation 2."); //diplayed as output
break;
default :
printf("Invalid Choice"); //diplayed as output
}
getch();
}
OUTPUT:
You have selected operation 1.






0 Comments
If you have any doubts , Please let me know.